Vazguard®
Browse all Indena’s documents about products, events, company information and so much more.
Go to sectionPeer-reviewed science on Vazguard®
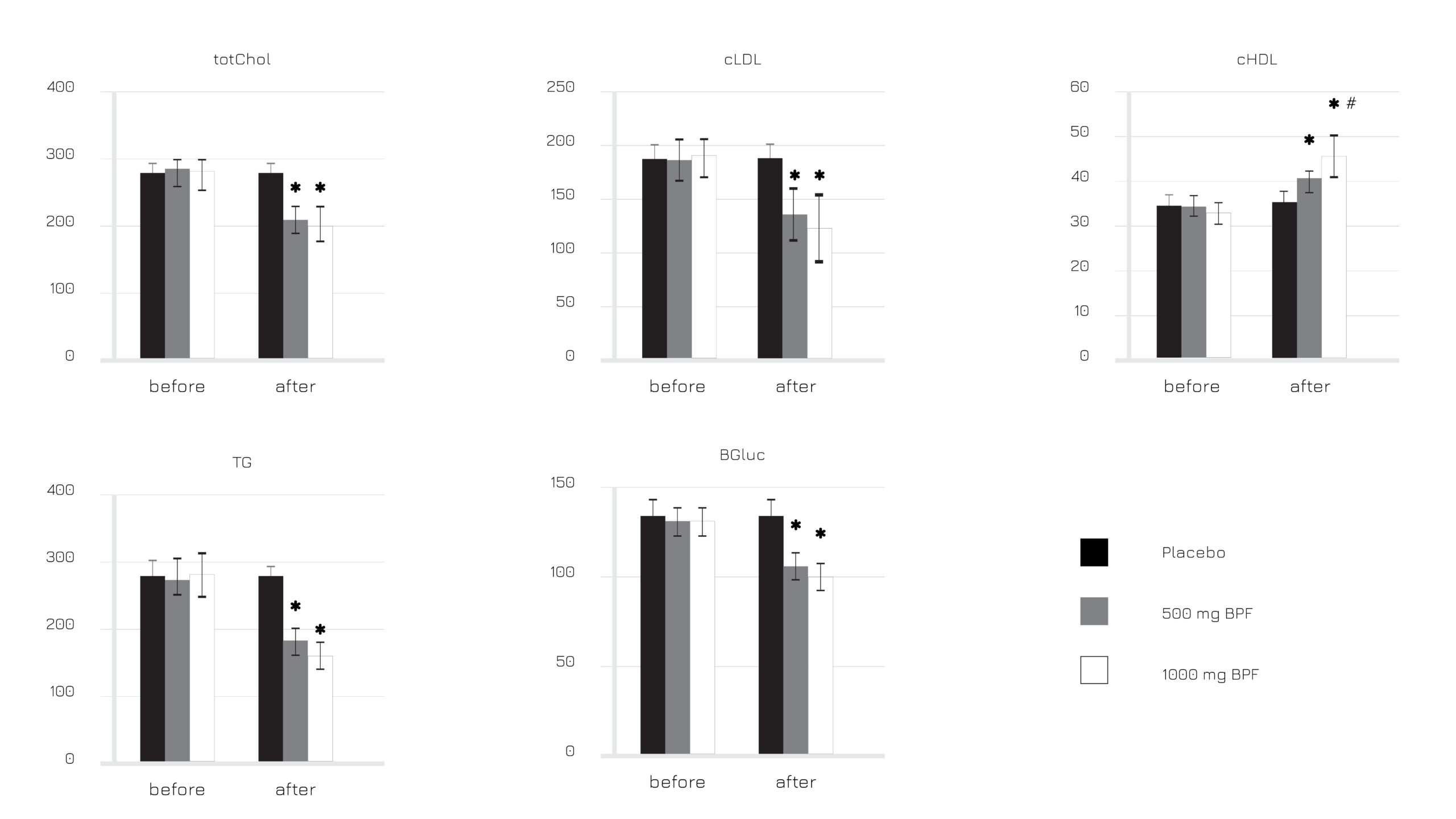
In a double-blind placebo-controlled study, Vazguard® could significantly optimize by -12% the abdominal fat in healthy volunteers:
- significant results could be observed within 1 month
- the optimization of abdominal fat translated into a global improvement of the glycolipidemic profile
- the LDL/HDL cholesterol was significantly optimized
- a beneficial effect was also observed on lipoproteins Apo-A and Apo-B
- the improvement of the lipid profile could also be observed in a wide population in terms of age and gender.
- a moderate optimization of glycemia was observed, along with a more significant beneficial effect on insulin resistence parameters (HOMA), thus suggesting a support of Vazguard® on the control of appetite
- the supplementation supported also the normalization of liver function as reflected by transaminases
Vazguard® showed potential efficacy in decreasing Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, the intestinal microbiota associated with obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular risk.
Figure 1: Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) effect on total cholesterol (totChol), LDL cholesterol (cLDL), HDL cholesterol (cHDL), tryglicerides (TG) and blood glucose (BGluc), before and after the intervention.
Vazguard® demonstrated to have an activity on gut microflora involved in genesis of abdominal fat, obesity and diabetes.
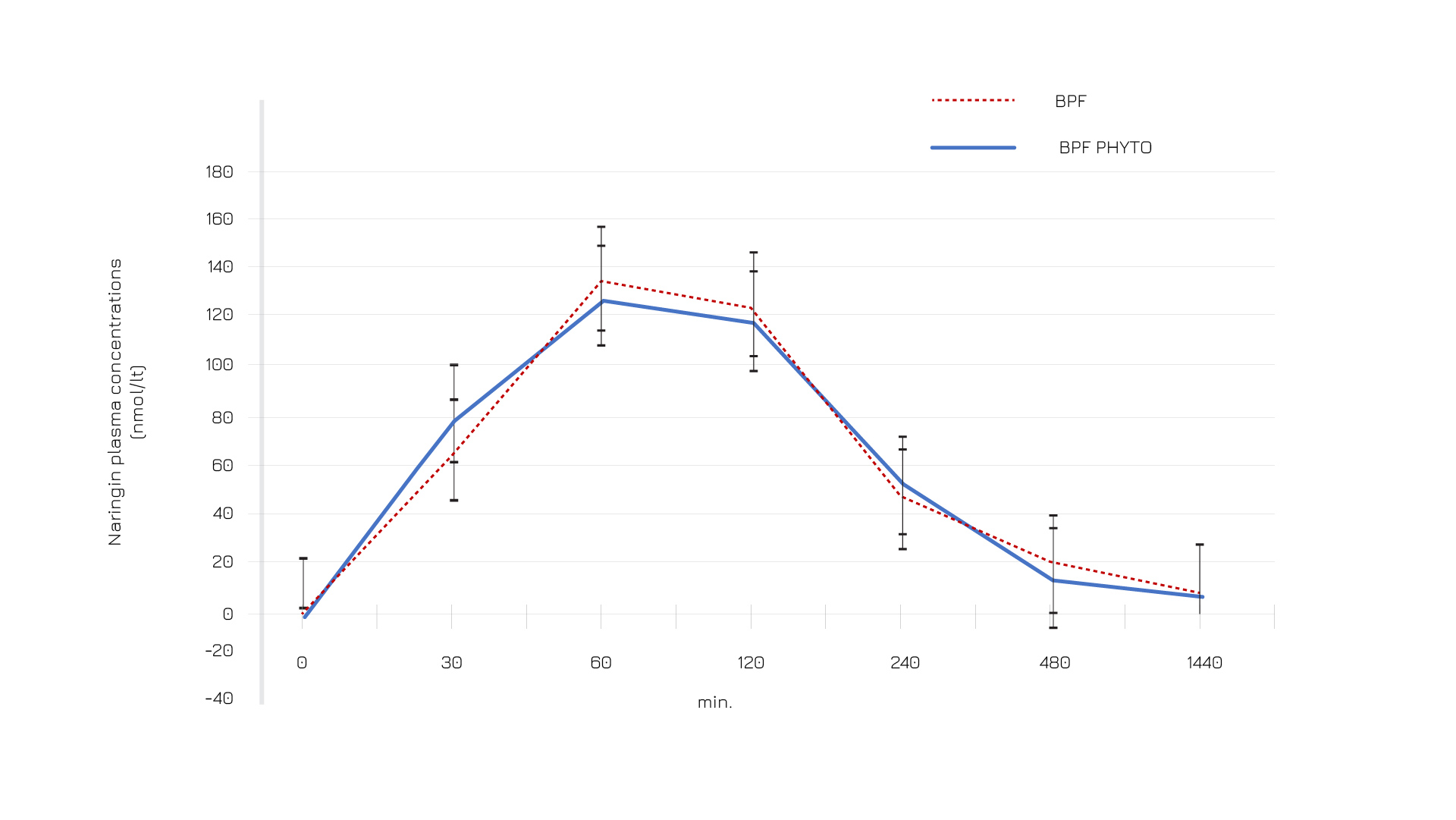
The Phytosome formulation of the BPF shows an optimal absorption compared to the standard formulation. A human study on 60 participants, 20 receiving Vazguard®, demonstrates a 2.5-fold increase in its bioabsorption compared to the non-Phytosome formulation.
In case of use of Phytosome delivery system, a significant levelling of fasting plasma glucose, serum cLDL and triglycerides accompanied by a valuable leverage of cHDL level is observed, too.
Figure 2: Plasma naringin profile after ingestion of standard Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) and Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) Phytosome formulation.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1- Formisano C. et al,J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167;
2- Di Donna L et al J Nat Prod 72:1352–1354 5 (2009)
3- Mollace V. et al.,Endocrine Metabolic& Immune Disorders – Drug Targets 2019, 19, 136-143;
4- Rondanelli M. et al., Phytotherapy Res. 2020, in press;
5- Ramaschi G.,et al, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167
6- Riva A. et al., J Appl.Microb Res. 2020, 3 (2), 45-51.
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.