Berbevis® – Berberine Indena Phytosome™
Browse all Indena’s documents about products, events, company information and so much more.
Go to sectionA pharmacokinetic study has shown Berbevis® greatly favors berberine’s bioaccessibility profile (AUC) on molar basis and with observed dose linearity. The pharmacokinetic profile of total and free berberine after the administration of Berbevis®and of berberine chloride to healthy volunteers was tested in a study with twelve healthy volunteers of both sexes with a mean age of 29 ± 7.72 and a mean BMI of 23.09 ± 1.27.
A human randomized-controlled, double-blind, versus placebo trial with Berbevis® showed that a 60-day supplementation may help support the balance of blood sugar levels in individuals with challenged fasting glucose. Participants who took the ingredient experienced a favorable shift in fasting glycemia compared to those receiving the placebo.
Lipid values also followed a positive trend. Total cholesterol, triglycerides, and the cholesterol/HDL ratio moved in a more balanced direction in the supplemented group, suggesting a potential benefit for metabolic well-being.
Regarding insulin and glucose management, the data indicated a more favorable pattern in both insulin levels and the HOMA index—an important marker of insulin resistance.
Furthermore, the ApoB/ApoA ratio and total cholesterol values, showed a meaningful adjustment in the Berbevis® group: this shift may reflect a healthier lipid profile, which could contribute to maintain an overall lipid metabolism in shape.
In terms of body composition, participants receiving Berbevis® showed a tendency toward lower levels of: visceral fat, total fat mass and waist circumference.
The supplementation was well tolerated throughout the study, with no reported side effects.
Peer-reviewed science on Berbevis®
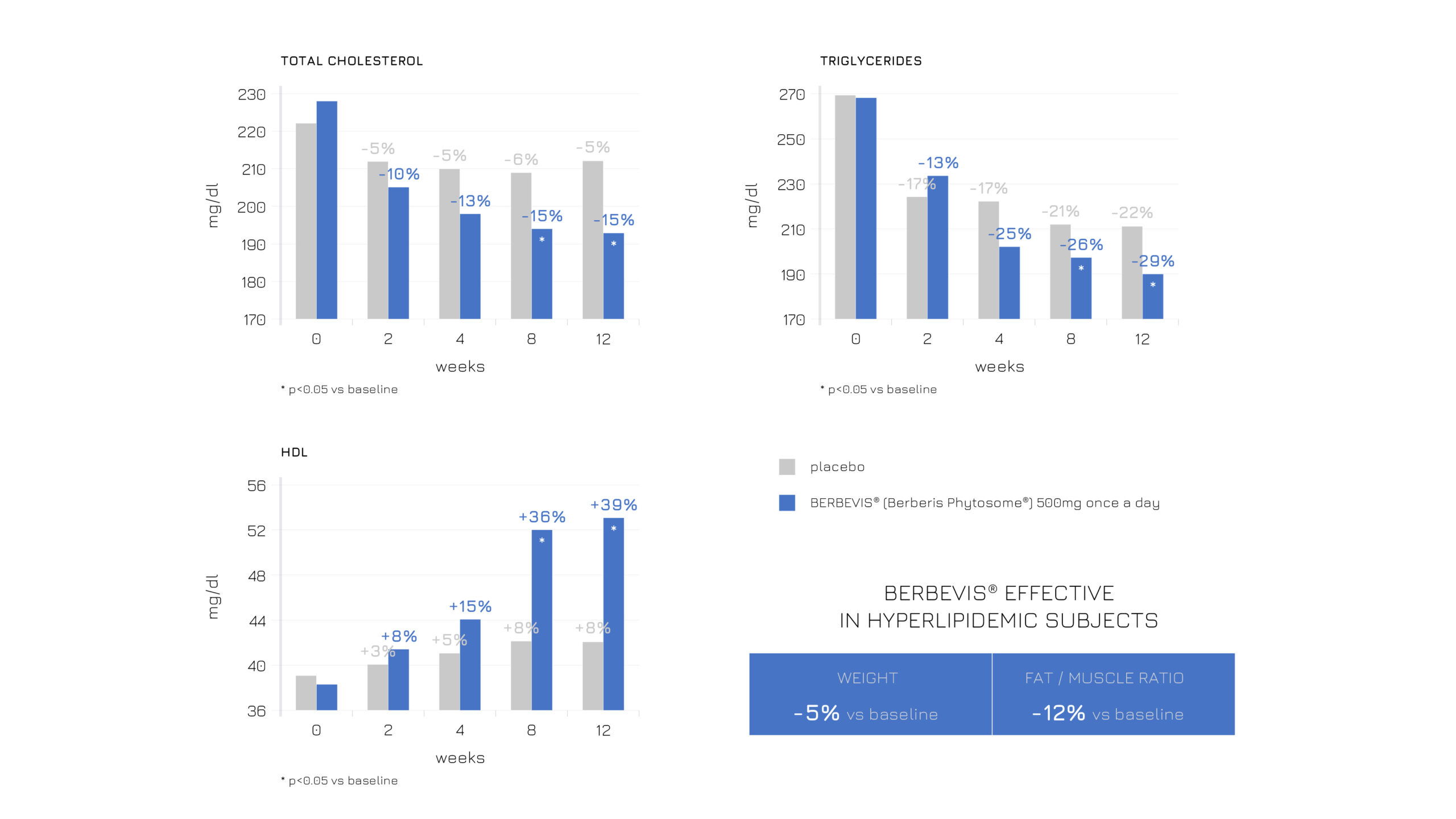
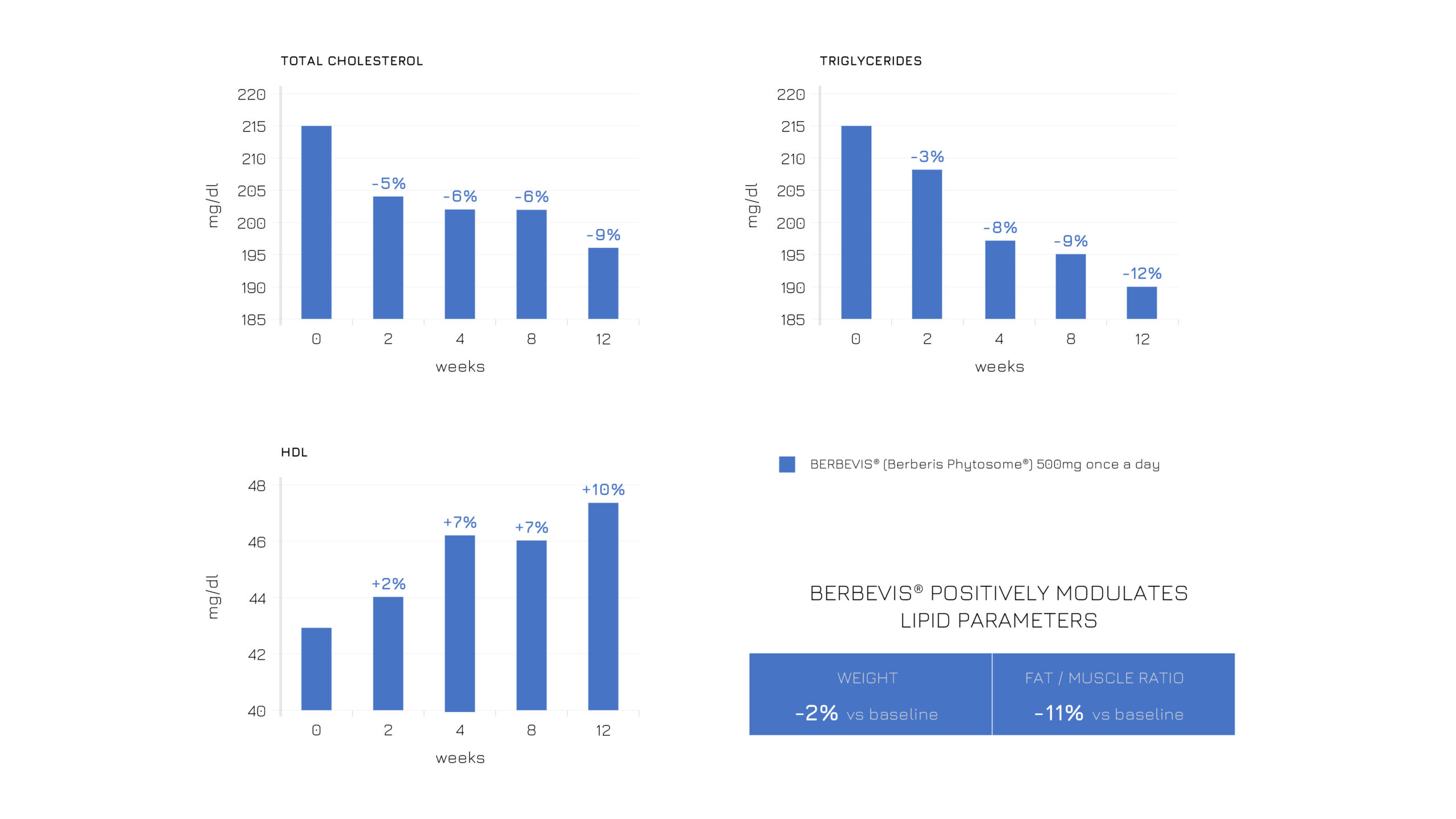
Berbevis® has already proven its effectiveness in modulating body composition and balancing the lipid profile. A recent study further validates that all its positive effects can be achieved with a single daily 550-mg dose. Specifically, the study administered Berbevis® to two different populations: subjects with stable hyperlipidemia (n=47; SM + Berbevis® vs SM + placebo) and with occasional hyperlipidemia (n=25; SM + Berbevis® vs baseline). In both cases, Berbevis® showed a positive influence on body composition and lipid profile (see Figures 1 and 2).
Figure 1: Effects of a single daily dose of Berbevis® in stably hyperlipidemic subjects, considering HDL, total cholesterol, TG and body composition (weight and fat/muscle ratio).
Figure 2: Effects of a single daily dose of Berbevis® in occasionally hyperlipidemic subjects, considering HDL, total cholesterol, TG and body composition (weight and fat/muscle ratio).
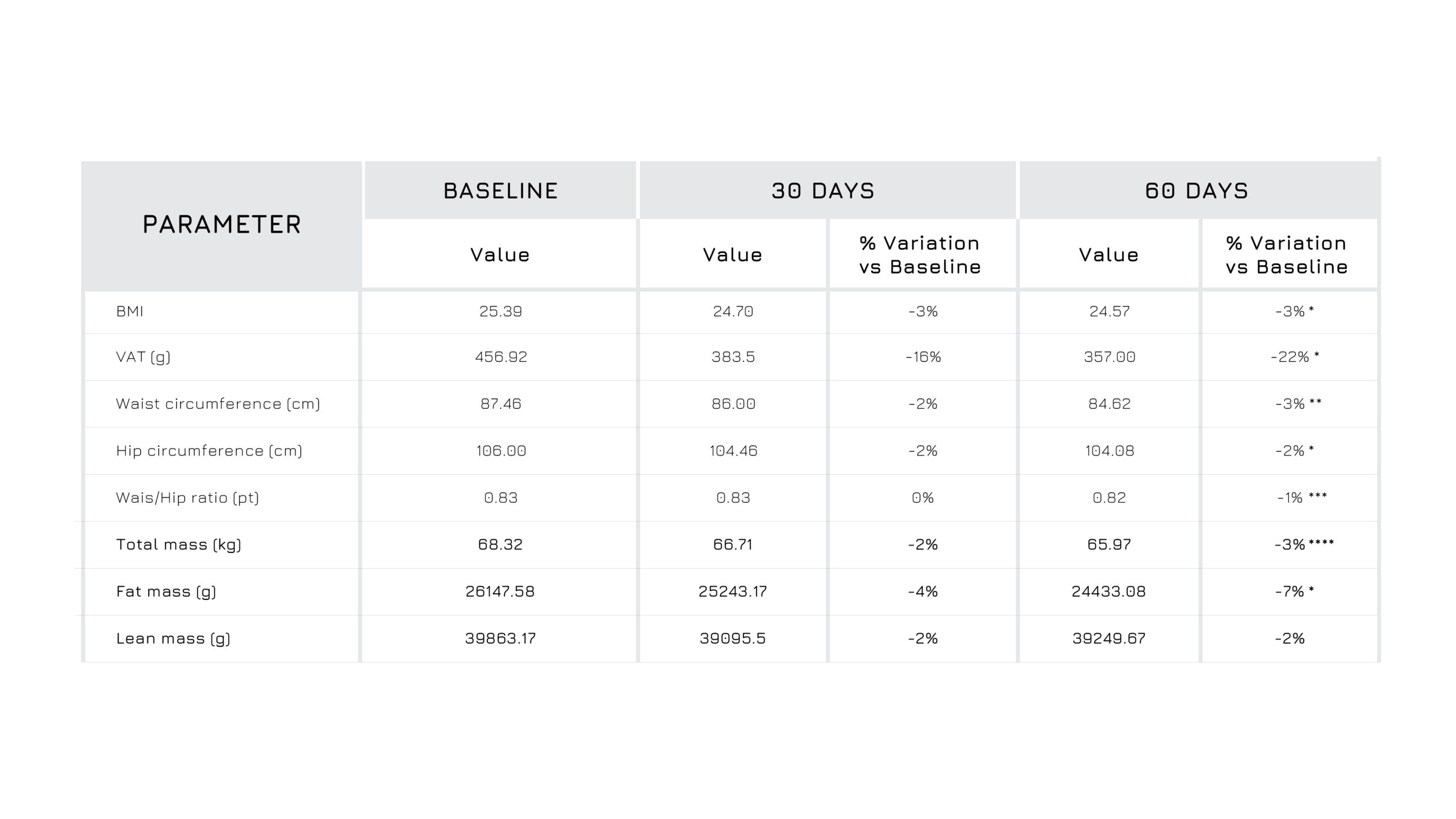
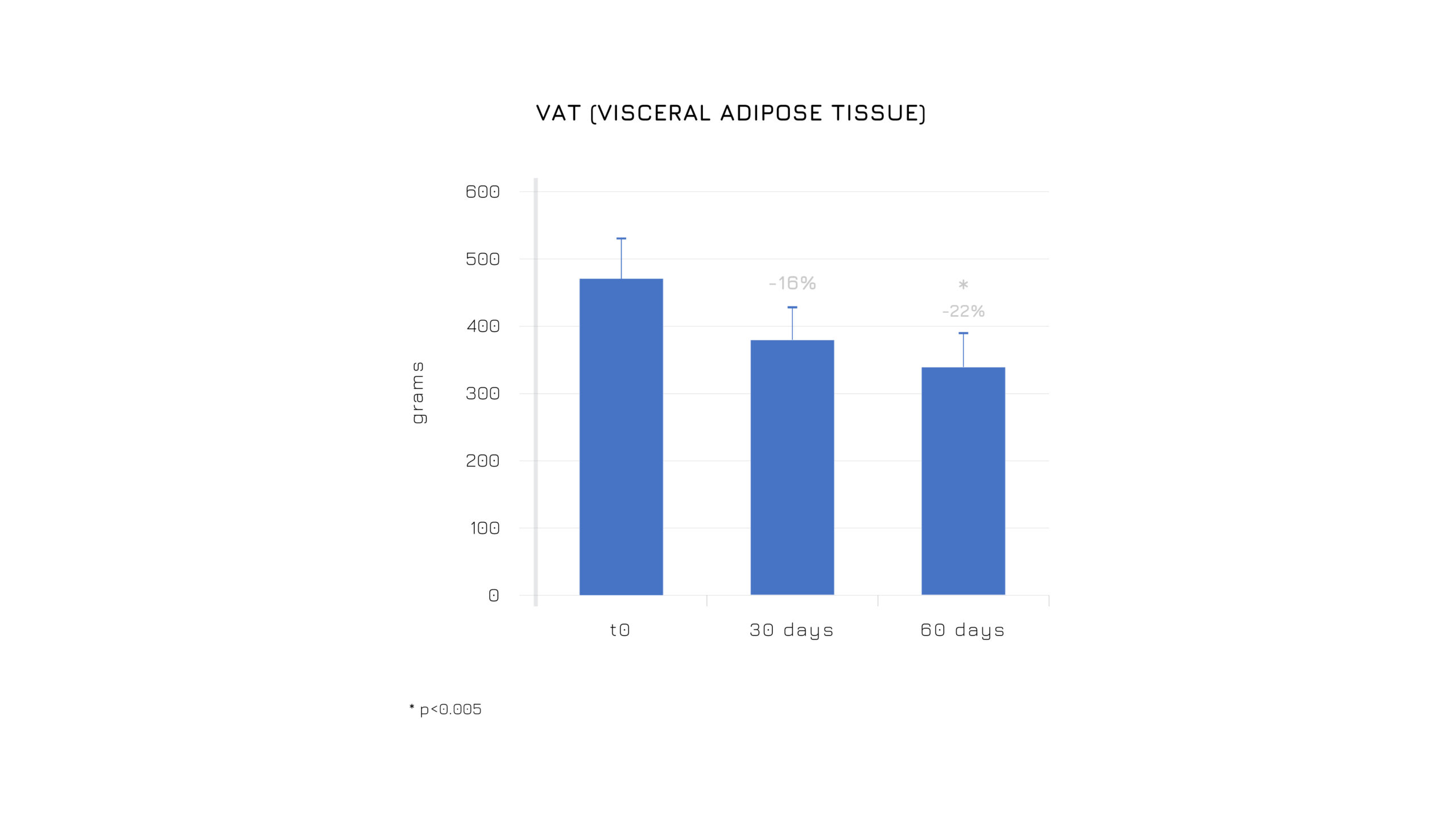
Berbevis® has a positive effect on body composition, inducing a redistribution of adipose tissue even if enrolled subjects aren’t under low calories diet (Figure 3,4)2.
Figure 3. Descriptive statistics for the body composition measured at baseline (t0) and after 60 days (t2) of Berbevis® supplementation.W/H: Waist/Hip Ratio; BMI: Body Mass Index. *p<0.05; **p<0.005.
Figure 4. Effectiveness on body composition, inducing a redistribution of adipose tissue with the reduction of the visceral fat tissue and fat mass. *p<0.005.
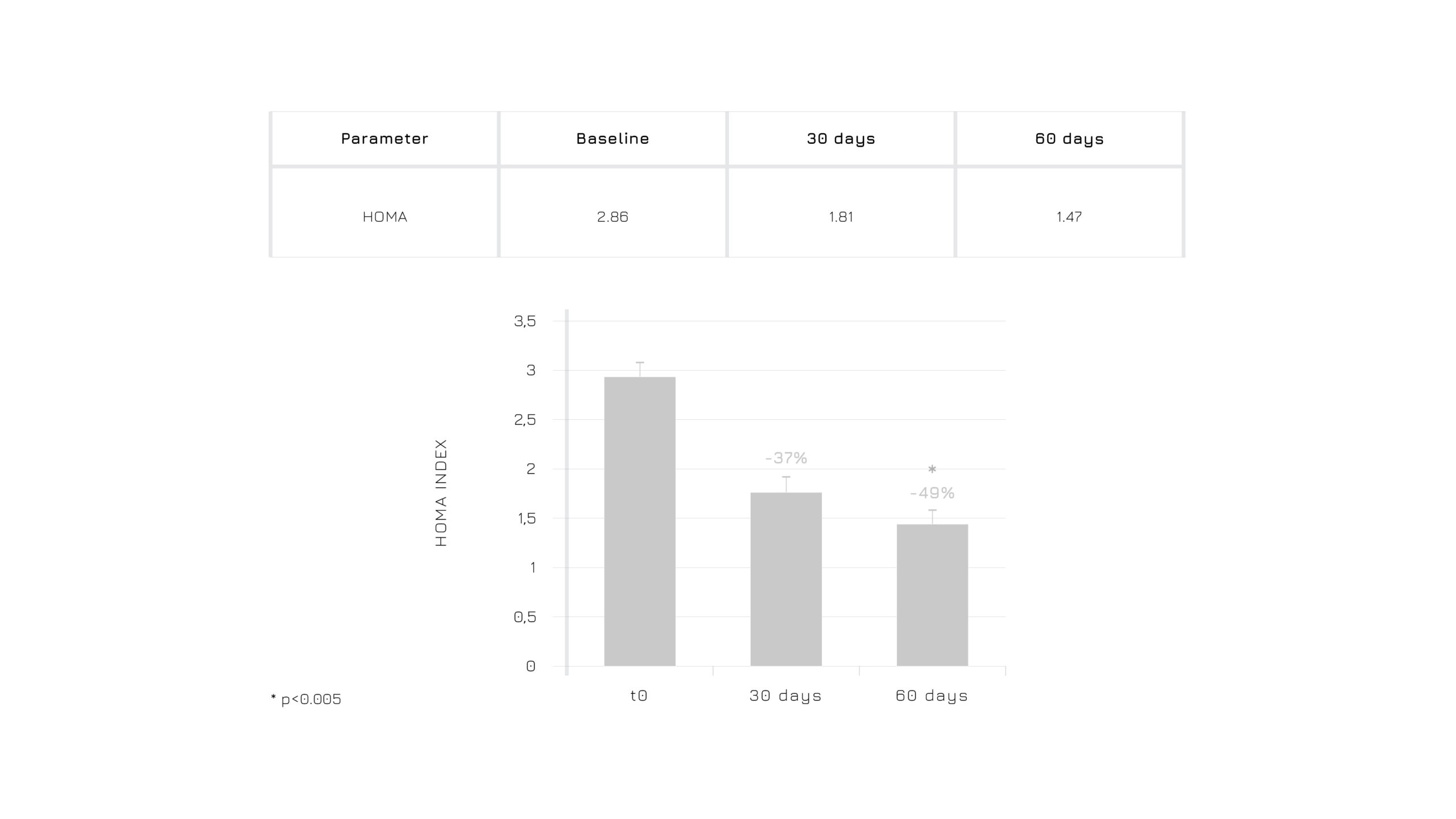
Berbevis®significantly modulates insulin resistance (HOMA index) after 30 days of supplementation (Figure 5). The homeostatic model assessment (HOMA) is a mathematical formula correlating blood glucose and insulin. It’s a validated method used to quantify insulin resistance and function of pancreatic beta-cells (which produce insulin). The higher is the HOMA score, the higher is the risk of insulin resistance.
Figure 5. Effect of Berbevis® on HOMA index in PCOS individuals (*p≤0.005).
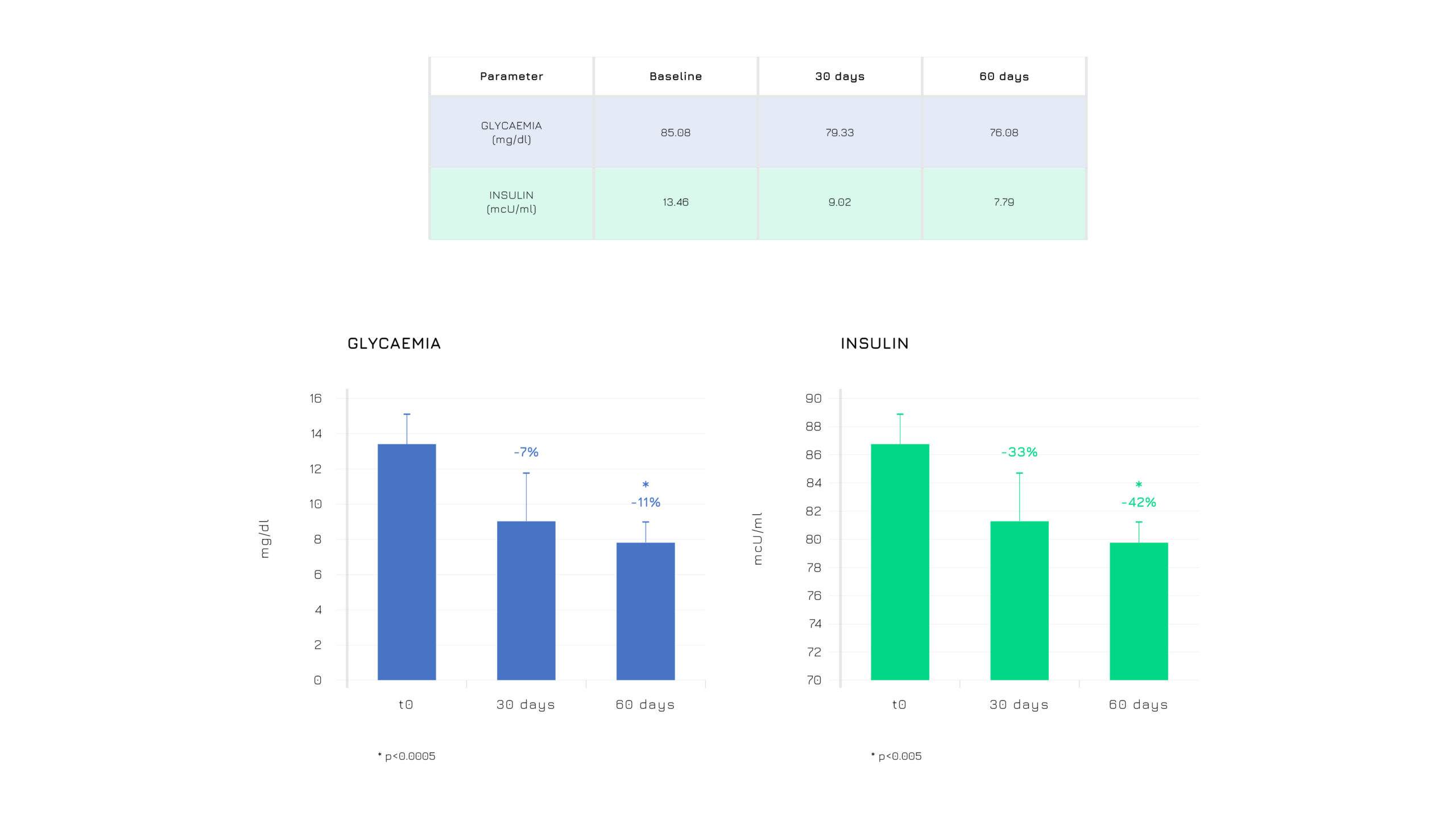
Berbevis® significantly improves blood sugar profile optimizing both glucose and insulin (Figure 6)2.
Figure 6. Effect of Berbevis® on the glycemic profile in PCOS individuals (*p≤0.005; **p<0.0005).
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1Petrangolini G. et al. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov
2Rondanelli M, et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Jul;27(14):6718-6727.
3Cesarone MR, et al. Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino).70(1):10-15. (2024).
4Rondanelli M, et al.Nutrients 13 (2021)
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.