Vazguard®
浏览有关 Indena 产品、活动、公司信息等的所有文档。
前往查看经过同行评议的科学研究
In a double-blind placebo-controlled study, Vazguard® could significantly optimize by -12% the abdominal fat in healthy volunteers:
- significant results could be observed within 1 month
- the optimization of abdominal fat translated into a global improvement of the glycolipidemic profile
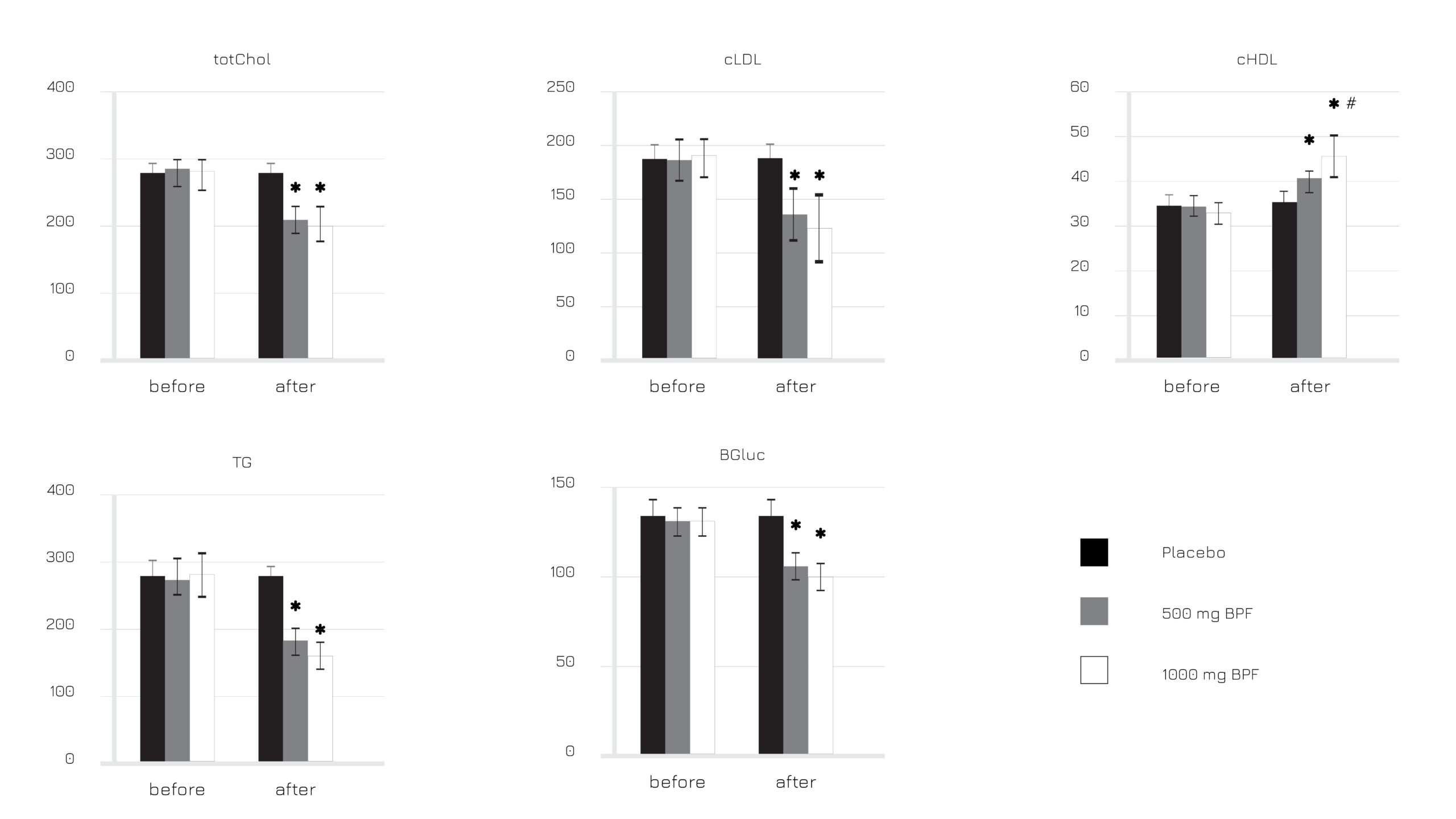
- the LDL/HDL cholesterol was significantly optimized
- a beneficial effect was also observed on lipoproteins Apo-A and Apo-B
- the improvement of the lipid profile could also be observed in a wide population in terms of age and gender.
- a moderate optimization of glycemia was observed, along with a more significant beneficial effect on insulin resistence parameters (HOMA), thus suggesting a support of Vazguard® on the control of appetite
- the supplementation supported also the normalization of liver function as reflected by transaminases
Vazguard® showed potential efficacy in decreasing Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes, the intestinal microbiota associated with obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular risk.
Figure 1: Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) effect on total cholesterol (totChol), LDL cholesterol (cLDL), HDL cholesterol (cHDL), tryglicerides (TG) and blood glucose (BGluc), before and after the intervention.
Vazguard® demonstrated to have an activity on gut microflora involved in genesis of abdominal fat, obesity and diabetes.
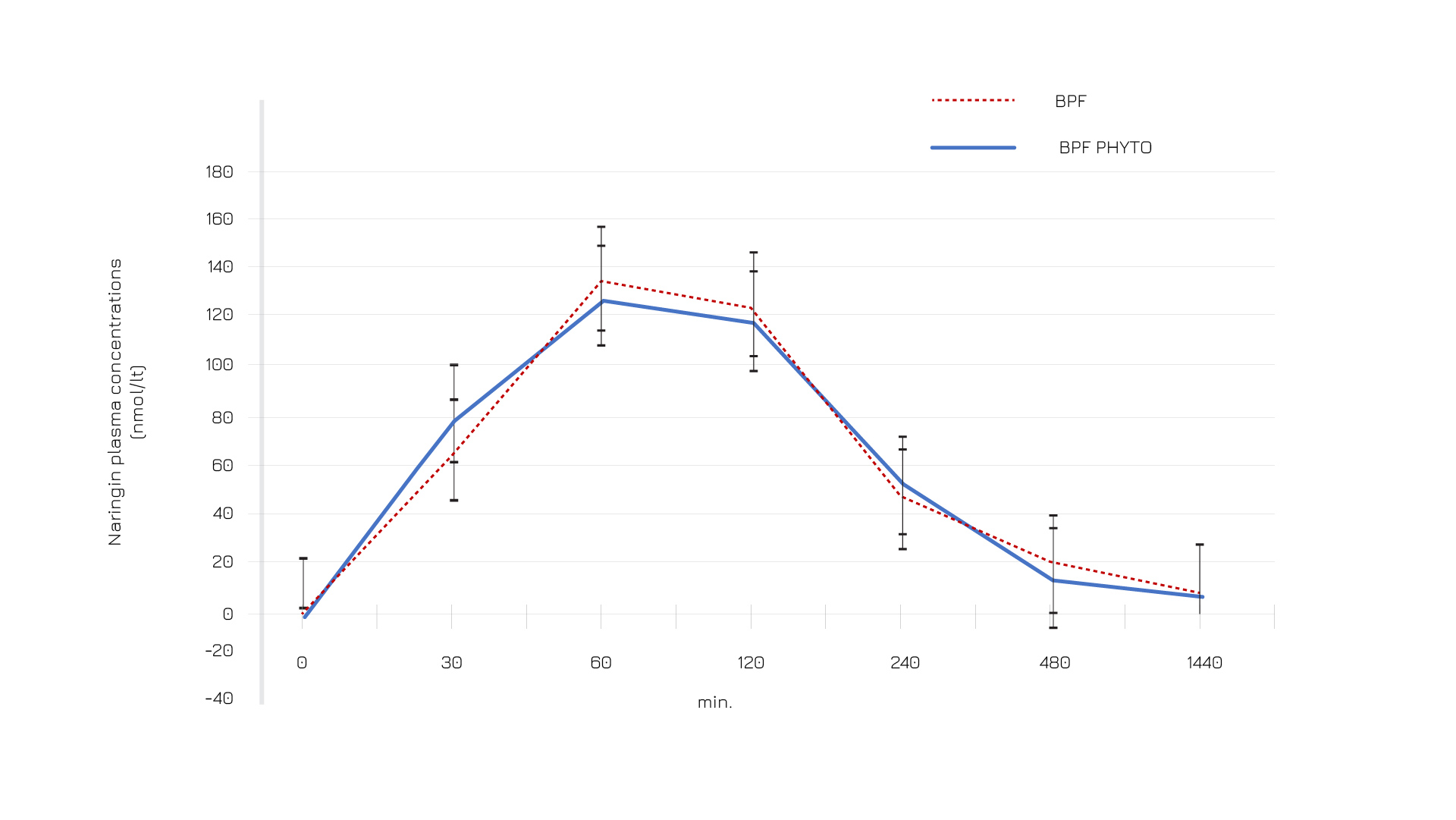
与标准提取物相比,BPF的 Phytosome®配方显示出更高的口服生物利用度。一项对 60名志愿者(其中 20名接受 VAZGUARD®)的研究表明,与非 Phytosome®配方相比,其生物利用度提高了 2.5倍。
在使用 Phytosome®技术的情况下,还观察到空腹血糖、血清 cLDL和甘油三酯的显着改善,同时 cHDL水平的变化也有显著的临床意义。
Figure 2: Plasma naringin profile after ingestion of standard Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) and Bergamot Polyphenol Fraction (BPF) Phytosome® formulation.
参考文献
1- Formisano C. et al,J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167;
2- Di Donna L et al J Nat Prod 72:1352–1354 5 (2009)
3- Mollace V. et al.,Endocrine Metabolic& Immune Disorders – Drug Targets 2019, 19, 136-143;
4- Rondanelli M. et al., Phytotherapy Res. 2020, in press;
5- Ramaschi G.,et al, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3159−3167
6- Riva A. et al., J Appl.Microb Res. 2020, 3 (2), 45-51.
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.