Ubiqsome®
Browse all Indena’s documents about products, events, company information and so much more.
Go to sectionA study evaluating the solubility and oral absorption of Ubiqsome® in human volunteers has shown - on molar basis - 9 fold better bioabsorption (AUC) of coenzyme Q10 with Indena PhytosomeTM after only one supplementation compared to unformulated CoQ10.
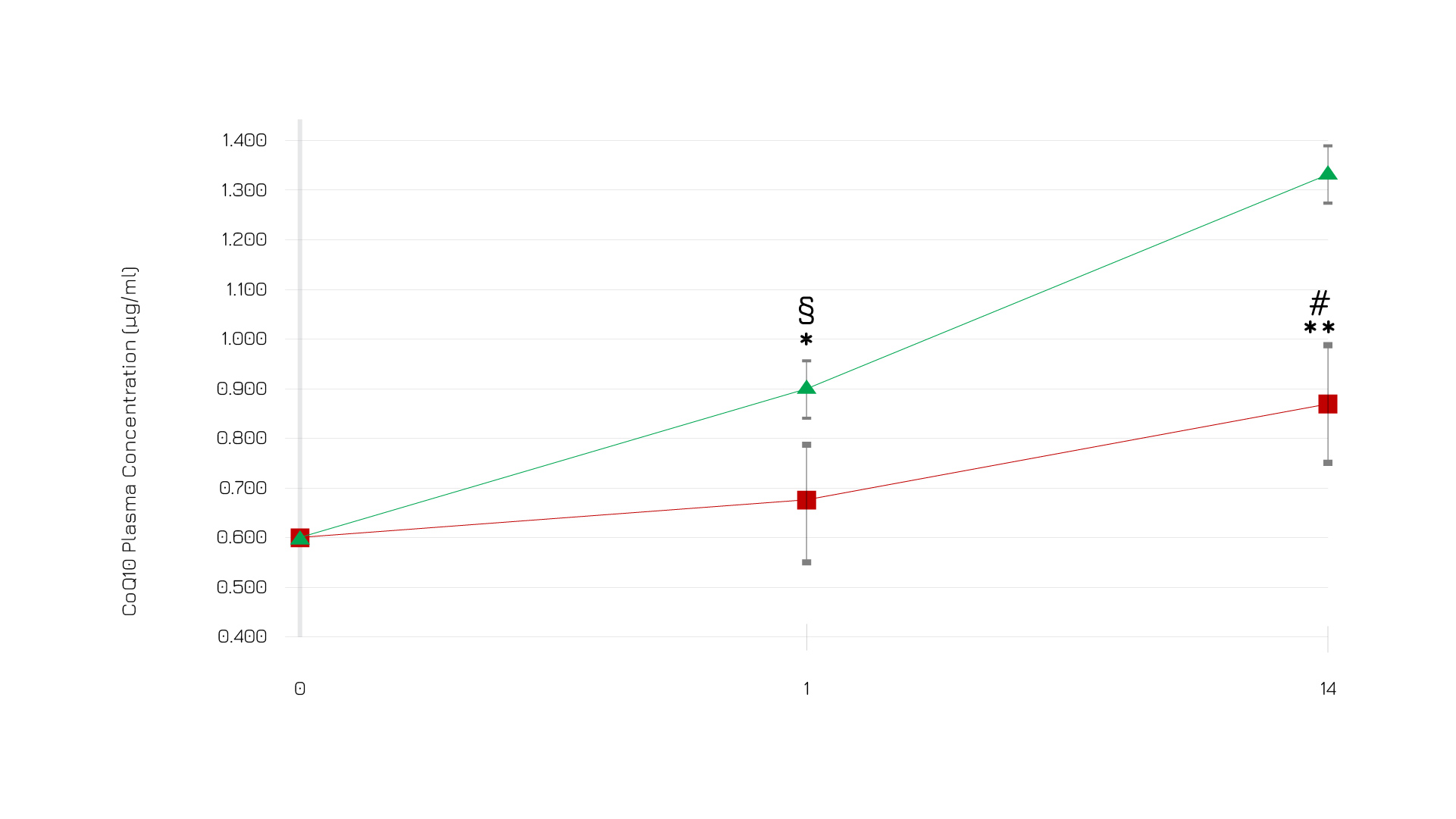
In a second study, the repeated supplementation with 150 and 300 mg of Ubiqsome® has demonstrated a dose-dependent increase in CoQ10 plasma concentration levels vs baseline, reaching up to +116% increase after 14-days (p<0,0001). (Fig 1)
Figure 1: CoQ10 plasma levels after Ubiqsome® repeated supplementation in volunteers. Red squares - 150 mg/day; Green triangles - 300 mg/day
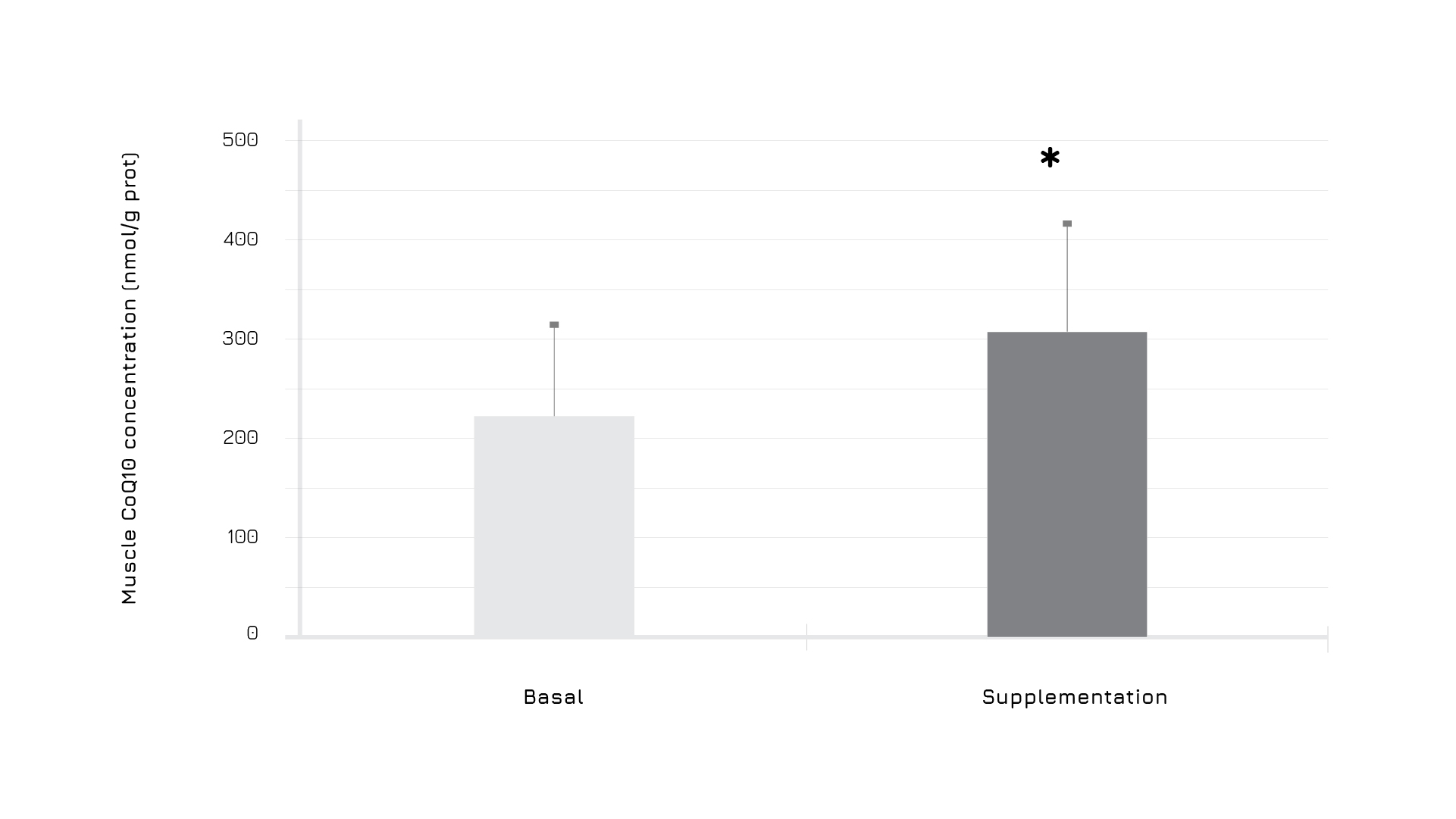
In a human study conducted on healthy athletes over 50 years old performing a complete training session in a climatic chamber, Ubiqsome® significantly (p<0,05) optimized CoQ10 levels in muscles by +36% (Figure 2).
Moreover, it improved the total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and favorably controlled biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation.
Figure 2: Effect of exercise and Ubiqsome® supplementation on CoQ10 levels in muscle.
Ubiqsome®, with its enhanced CoQ10 antioxidant activity, supports muscle function under physical and athletic stress, and helps preserve muscle health during prolonged therapies such as statins or GLP-1 agonists.
A double blind randomized, placebo-controlled clinical study enrolled 60 subjects experiencing statin-associated asthenia, to assess the effects on muscle strength of dietary supplementation with Ubiqsome®.
At each time-step for 8 weeks, the treated group and the placebo group were administered with 3 physical tests: handgrip test (HGT), 1-minute sit-to-stand repetition (STS), 2-minute step test (2MST). Subjects’ asthenia levels were measured using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS).
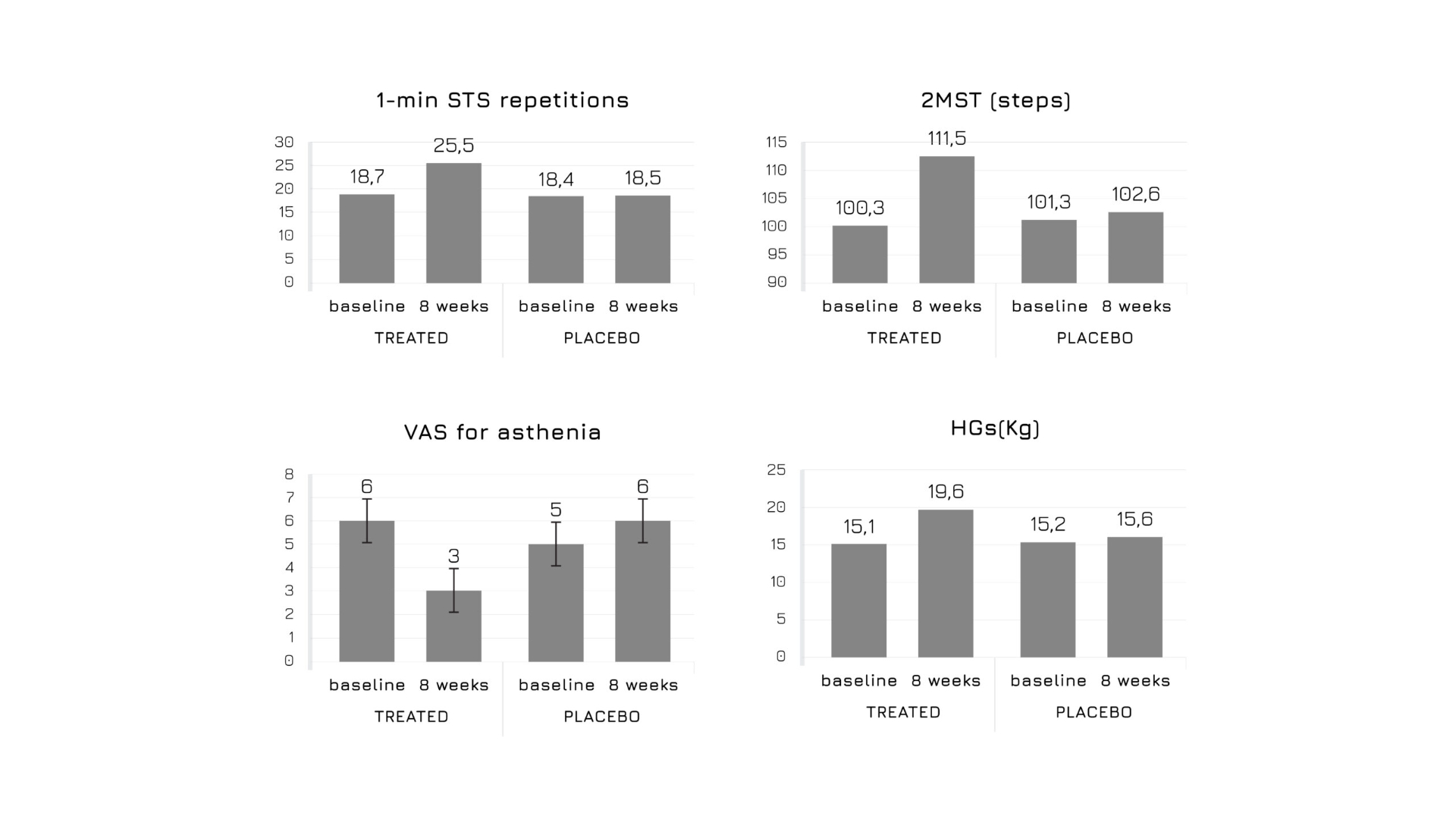
At the end of the study, people following the Ubiqsome® supplementation regimen (150 mg of Ubiqsome® twice a day) reduced by half the asthenia sore, while experiencing an amelioration in HGT (+29.8 ± 3.6%), 1-min STS repetitions (+36.4 ± 3.9%), and 2MST (11.1 ± 1.8%) (p <0,05 vs baseline and vs placebo) (Fig. 3).
Figure 3: HGT, VAS,1-min STS repetitions, and 2MST in Ubiqsome® and placebo groups at baseline and after 8 weeks.
Only if properly delivered, oral CoQ10 can support skin cellular energy from within: Ubiqsome® is the right example.
In an ex-vivo study vs unformulated coenzyme Q10, Ubiqsome® demonstrated significantly higher absorption efficiency in human dermal cells.
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) were taken from the plasma of subjects who received either the Indena PhytosomeTM formulation (Ubiqsome®) or the crystalline form of CoQ10, and were incubated with cell line.
The Indena PhytosomeTM delivery system demonstrated superior bioabsorption and cellular uptake. This resulted in CoQ10 being delivered to human dermal fibroblasts more efficiently - 9x vs baseline - and 2x vs traditional CoQ10.
Endothelial function is an important early marker for cardiovascular health, reflecting the ability of the endothelial layer to fight early pro-atherosclerosis conditions.
Since endothelial dysfunction is primarily driven by oxidative stress (like Reactive oxygen species - ROS and NO deficiency), the antioxidant potential of Ubiqsome® is a valuable ally to maintain the endothelium in good health.
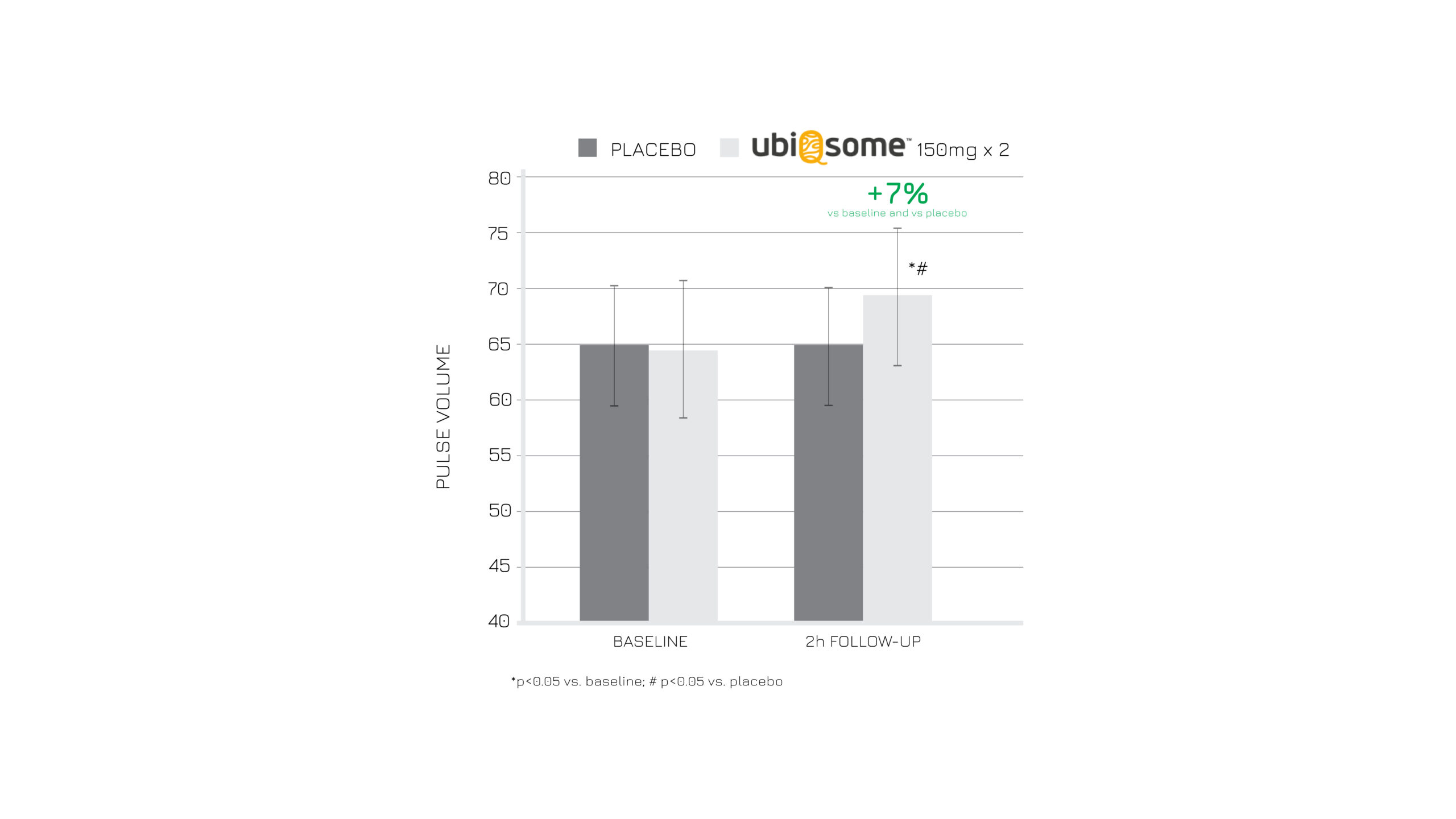
A scientific evidence on healthy young people has confirmed this hypothesis, showing the optimization of endothelial function (+7% p<0,05) both in acute and chronic settings after the supplementation of Ubiqsome® (Fig. 5).
Figure 5: Acute evaluation of pulse volume, 2 hours after administration of Ubiqsome® or placebo.
An in-vitro evaluation on muscular and intestinal cell lines has confirmed that macropinocytosis could be the key mechanism for the internalization of Ubiqsome® at cellular level, since the use of a macropinocytosis inhibitor drastically reduced CoQ10 cellular content.
The same study also confirmed that the Indena PhytosomeTM delivery system enhances intracellular concentration of CoQ10, compared to the coenzyme alone (Fig. 6).
This confirms that the action starts from the cells.
Figure 6: Coenzyme Q10 determination in different cell lines after product incubation.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
1Petrangolini G, et al., Curr Drug Deliv.16(8):759-767 (2019).
2Drobnic F. et al., J Food Sci Nutr Res 3 (4):262-275 (2020).
3Fogacci F. et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine 13.13:3741 (2024).
4Marcheggiani F. et al., Antioxidants 12.4:964 (2023).
5Cicero AFG. et al., Biofactors. Sep;48(5):1160-1165 (2022).
6Rizzardi N. et al., Antioxidants 0.6: 927 (2021).
Sorry, our website doesn't support IE11 and older versions
For a better experience try a modern browser:
This is a private file, to request the download of this resource, please fullfill the fields below.